What is dicing in machining?
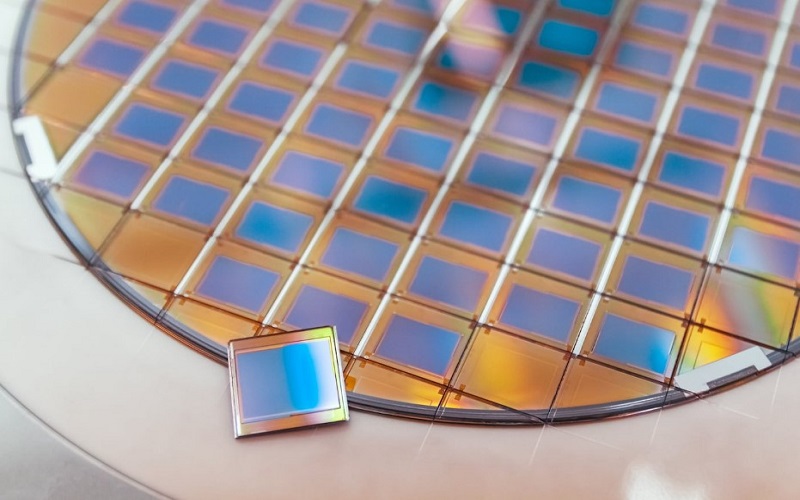
In machining, “dicing” refers to a specific process used primarily in the semiconductor and electronics industries to cut materials, such as silicon wafers, ceramics, glass, and other brittle materials, into precise, small, and often very thin pieces or components. The dicing process in machining is distinct from the wafer dicing process used in semiconductor manufacturing, as it is focused on various materials, not just semiconductor wafers.
Key features of dicing in machining include:
-
Material Compatibility: Dicing in machining can be applied to a wide range of materials, including semiconductors, ceramics, glass, and other brittle materials used in various industries.
-
Precision Cutting: Dicing machines are designed to make extremely precise cuts with tight tolerances. The goal is to produce components or parts with consistent dimensions and minimal edge chipping or damage.
-
Small Component Production: Dicing is often used to create small components or parts, which are then used in various electronic, optical, or mechanical devices. These components can range from microchips and MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) devices to optical lenses and electronic packages.
-
Methods of Dicing: Dicing machines employ various methods to cut materials, including:
-
Blade Dicing: Similar to the sawing process used in semiconductor wafer dicing, blade dicing involves the use of a rotating blade with abrasive particles to cut the material. This method is effective for many brittle materials.
-
Laser Dicing: Laser dicing uses a high-energy laser beam to precisely ablate the material along the desired cutting path. It is suitable for materials that may be sensitive to mechanical stress or for creating intricate and narrow cuts.
-
-
Applications: Dicing in machining finds applications in various industries, including electronics, optics, MEMS manufacturing, and precision engineering. For example, it is used to create individual electronic components, optical components like waveguides, and micro-scale mechanical parts.
-
Quality Control: Precision and quality control are critical in dicing processes. Manufacturers use inspection and measurement techniques to ensure that the cut pieces meet the required specifications and quality standards.
-
Wafer Singulation: In the semiconductor industry, the term “wafer singulation” is often used interchangeably with dicing in machining. It refers to the process of cutting a semiconductor wafer into individual chips or dice using specialized dicing equipment.
In summary, dicing in machining is a precision cutting process used to create small, precise components or parts from brittle materials. It is a crucial step in the manufacturing of a wide range of devices and products in industries where high precision and consistency are essential. The choice of dicing method (blade dicing or laser dicing) depends on the material being processed and the specific requirements of the application.



