Decoding the Mystery of Myasthenia Gravis: A Comprehensive Guide
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a chronic autoimmune neuromuscular disease that disrupts communication between nerves and muscles, leading to weakness and fatigue. This can significantly impact daily life, but with proper understanding and management, individuals with MG can live fulfilling lives.
Unraveling the Causes:
The exact cause of Myasthenia gravis remains a puzzle, but it is believed to involve a combination of factors:
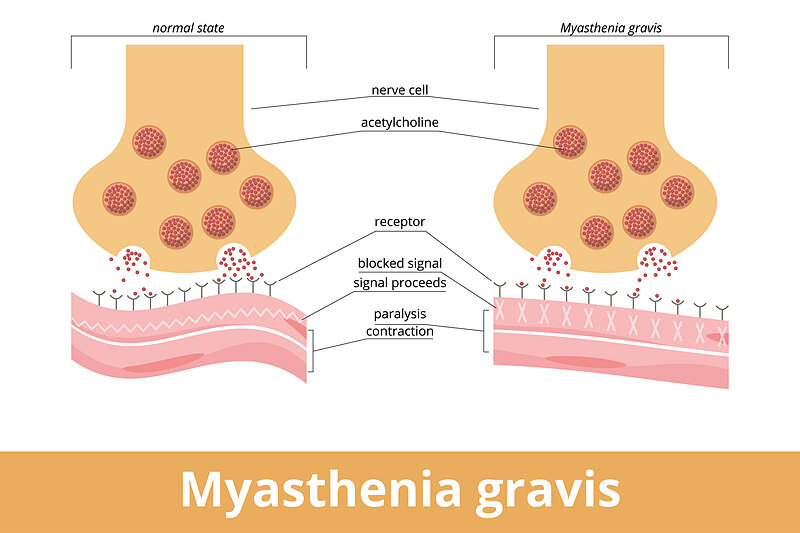
- Immune System Dysfunction: Antibodies mistakenly attack healthy tissue in the neuromuscular junction, the point where nerves meet muscles. This disrupts the transmission of nerve signals, leading to muscle weakness.
- Thymus Gland: The thymus, located in the chest, plays a role in immune system development. In some individuals with MG, the thymus is enlarged or overactive.
- Genetics: Having a family history of MG increases the risk of developing the disease.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms:
Myasthenia gravis symptoms can vary greatly from person to person and may fluctuate throughout the day or even week-to-week. Some common signs include:
- Muscle weakness: This is the hallmark symptom and can affect any muscle group, but most commonly affects the eyes, eyelids, face, throat, and limbs.
- Drooping eyelids (ptosis): This can make it difficult to open the eyes fully.
- Double vision (diplopia): This occurs when the muscles controlling each eye weaken differently.
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia): This can make it challenging to eat and drink.
- Speech difficulties: Slurred speech or a nasal voice can be caused by weakness in the muscles of the face and throat.
- Fatigue: This is a common symptom and can worsen with activity.
Diagnosing Myasthenia Gravis:
Diagnosing Myasthenia gravis can be complex and requires a combination of tests:
- Medical history and physical examination: The doctor will ask about symptoms and perform a physical exam to assess muscle weakness.
- Blood tests: These can detect antibodies associated with MG.
- Electrophysiological tests: These tests, such as the electromyography (EMG) and repetitive nerve stimulation (RNS), measure electrical activity in the muscles and nerves to confirm the diagnosis.
- Imaging tests: In some cases, imaging tests like a CT scan of the chest may be ordered to look for abnormalities in the thymus gland.
Treatment Options:
There is no cure for Myasthenia gravis, but effective treatment strategies can manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatment options may include:
- Medications:
- Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: These medications help to increase the amount of acetylcholine, a chemical that transmits nerve signals to muscles.
- Corticosteroids: These powerful anti-inflammatory medications can suppress the immune system and reduce muscle weakness.
- Immune-suppressing drugs: These medications can help to control the overactive immune system.
- Thymectomy: In some cases, surgery to remove the thymus gland may be recommended.
- Plasma exchange (PLEX): This procedure removes antibodies from the blood and can be helpful for managing severe MG symptoms.
- Physical and occupational therapy: These therapies can help to maintain muscle strength and function and adapt to limitations caused by MG.
Living Well with Myasthenia Gravis:
Living with Myasthenia gravis can be challenging, but with proper diagnosis, treatment, and support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Here are some tips for living well with MG:
- Build a strong relationship with your healthcare team: Regular checkups and communication with your doctor are crucial for managing symptoms and adjusting treatment plans as needed.
- Learn about your condition: Understanding how MG affects you empowers you to make informed decisions about your care.
- Adhere to your treatment plan: Taking medications as prescribed and attending therapy sessions are essential for managing symptoms and preventing complications.
- Manage stress: Stress can worsen MG symptoms. Relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation can be helpful.
- Join a support group: Connecting with others who understand what you are going through can provide emotional support and valuable advice.
- Stay active: Regular exercise within your tolerance can help maintain muscle strength and improve overall well-being.
- Maintain a healthy diet: Eating a nutritious diet can provide the energy you need and support overall health.
Looking Forward:
Research into Myasthenia gravis continues to advance, leading to new treatment options and a deeper understanding of the disease. With ongoing research and proper management, individuals with MG can look forward to improved treatment outcomes and a better quality of life.
for more information: fuseinfusion.com



